fungi life cycle asexual
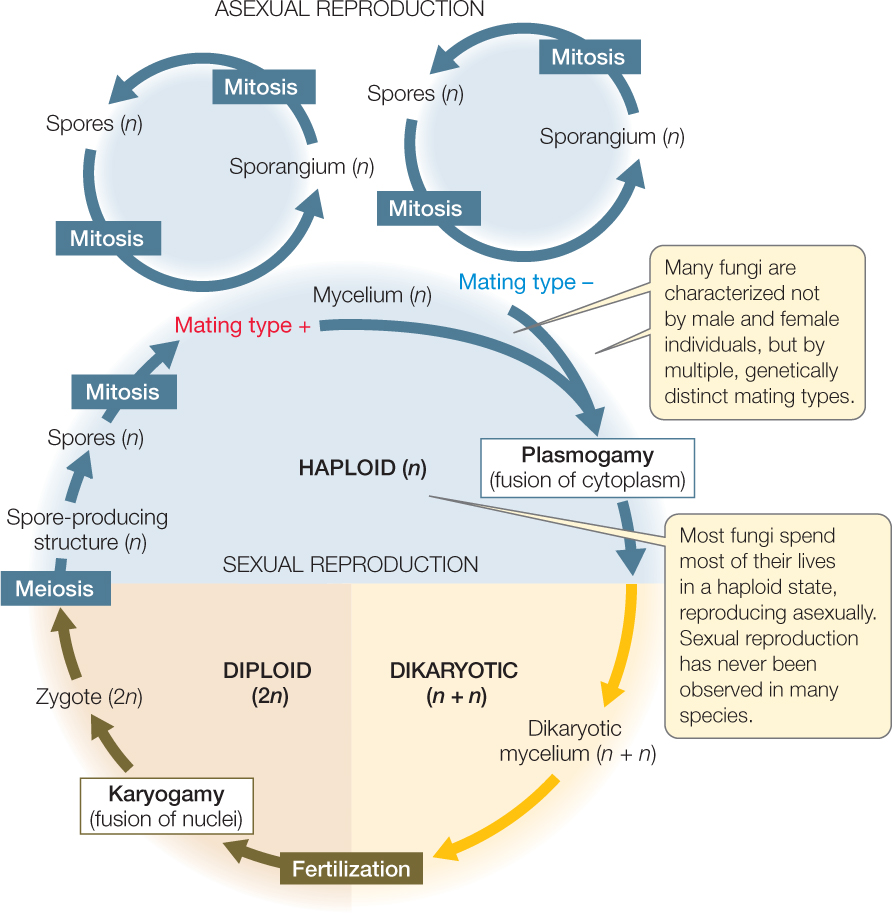
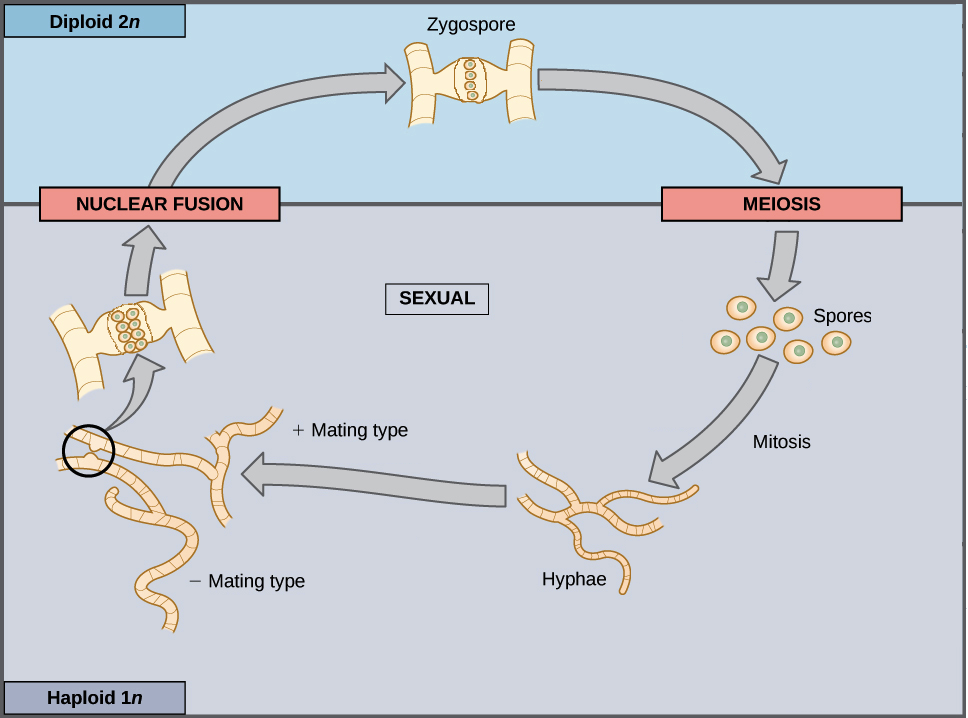
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins. Perfect fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually while imperfect fungi reproduce only asexually by mitosis.

Biology 197 Chapter 22 Exam 2 Sg Diagram Quizlet
In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
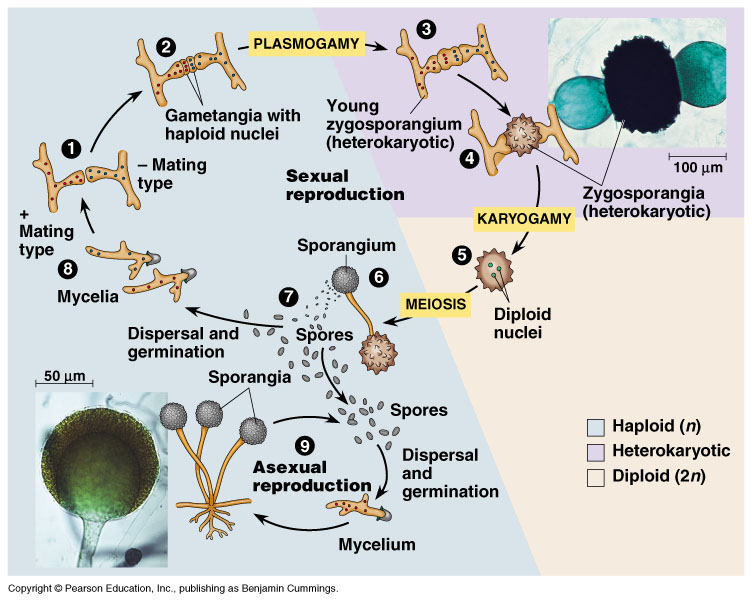
. Fungal thalli are shown in the figure at the beginning of this web page. This fungus presents in its life cycle two types of reproduction. In both sexual and asexual reproduction fungi produce.
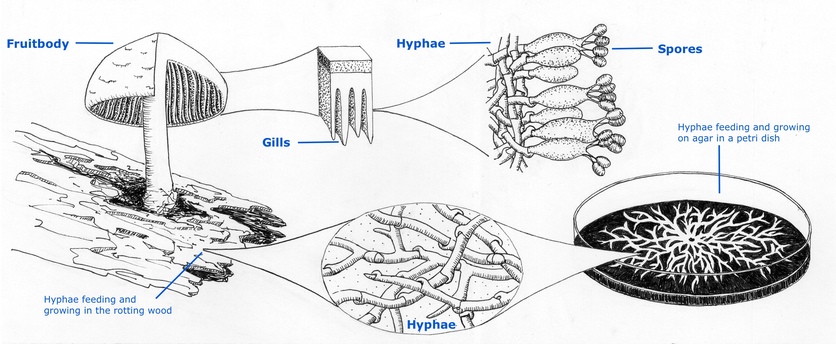
The organism grows and ramifies as typical fungal hyphae 5 to 10 µm in diameter. Asexual Reproduction of Fungi During the mycelium stage the fungus has the choice of reproducing sexually or asexually. The most common methods of asexual reproduction in addition to simple budding in yeasts are blastic development of conidia from specialized hyphae conidiogenous cells fragmentation.
In fungi with sexual and asexual phases the sexual phase is called the teleomorph and the asexual phase is called the anamorph. Fusion of nuclei from two opposite mating strains of the same species of fungus The sexual spores involved in fungis. Once the sexual union takes place sexual fruiting can occur causing more spores to repeat the cycle.
These are very resistant to high temperatures. These cells either remain. The life cycle begins when a haploid.
Life cycle of fungi. Asexual through the conidia and sexual mediated by ascospores. The single-celled zygote immediately goes through meiosis producing haploid cells that divide by mitosis.
Both sexual and asexual fruiting can take place causing fungi to spread and expand in. These are also called meiosporic and. During its asexual life cycle the fungus produces.
The asexual phase usually precedes the sexual phase in the life cycle and may be repeated frequently before the sexual phase appears. The sexual spores involved in fungis life cycle are formed by what. Fungus life cycle gametes fuse and form a diploid zygote.
The typical life cycle of filamentous fungi involves conidiation after a period of vegetative growth 1 2. Filamentous fungi produce several types of asexual spores such as.

Biology 2e Biological Diversity Fungi Characteristics Of Fungi Opened Cuny

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

Fungi Reproduction Cycle Structure How Do Fungi Reproduce Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Life Cycle Html 31 05fungilifecycle Jpg
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy
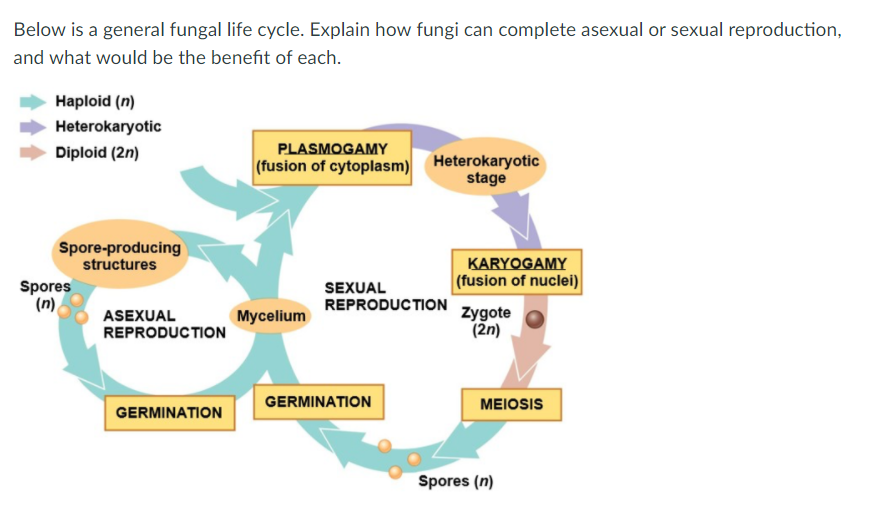
Solved Below Is A General Fungal Life Cycle Explain How Chegg Com

Fungus Reproductive Processes Of Fungi Britannica
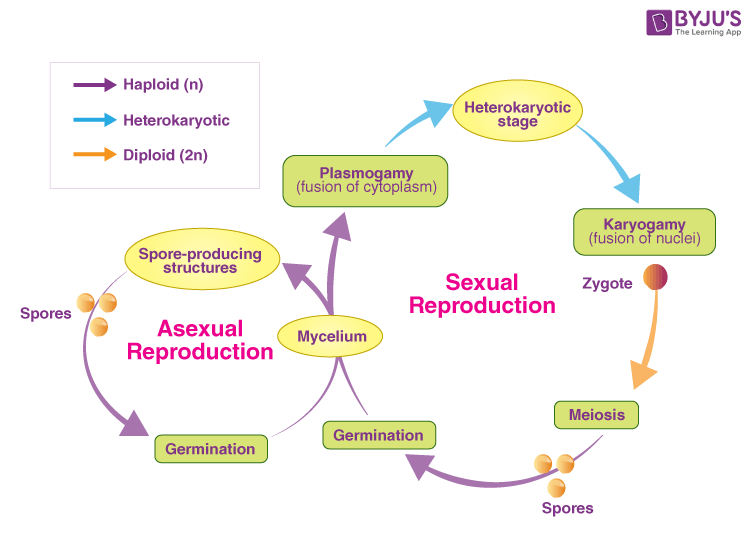
Fungi Life Cycle Introduction Life Cycle Faqs
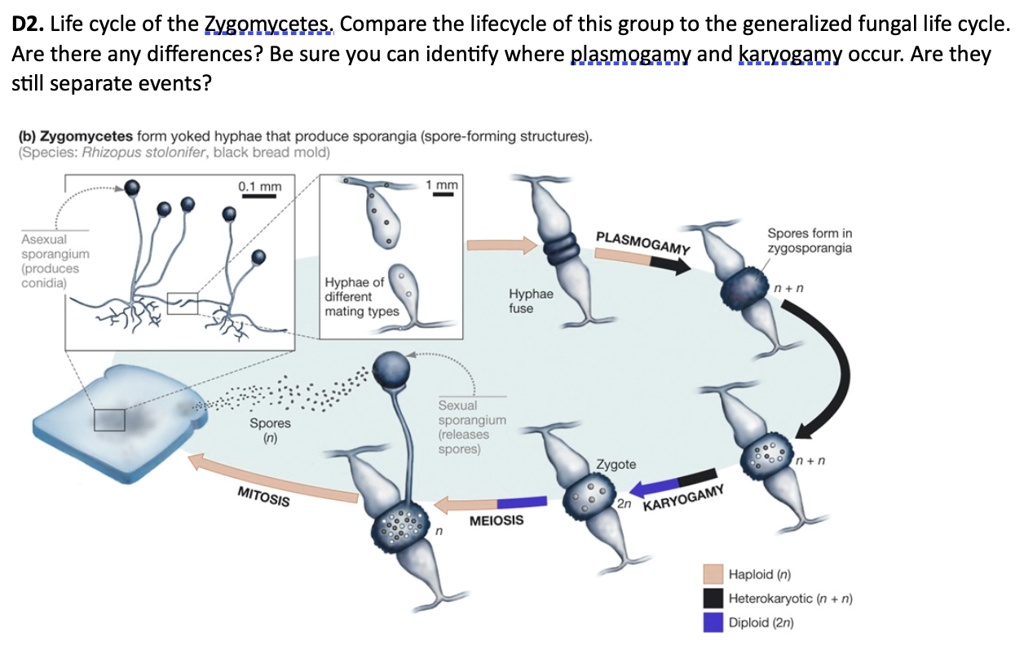
Solved D2 Life Cycle Of The Zygomycetes Compare The Lifecycle Of This Group To The Generalized Fungal Life Cycle Are There Any Differences Be Sure You Can Identify Where Plasmogamy And Karyogamy

Fungal Growth And Pathology Intechopen
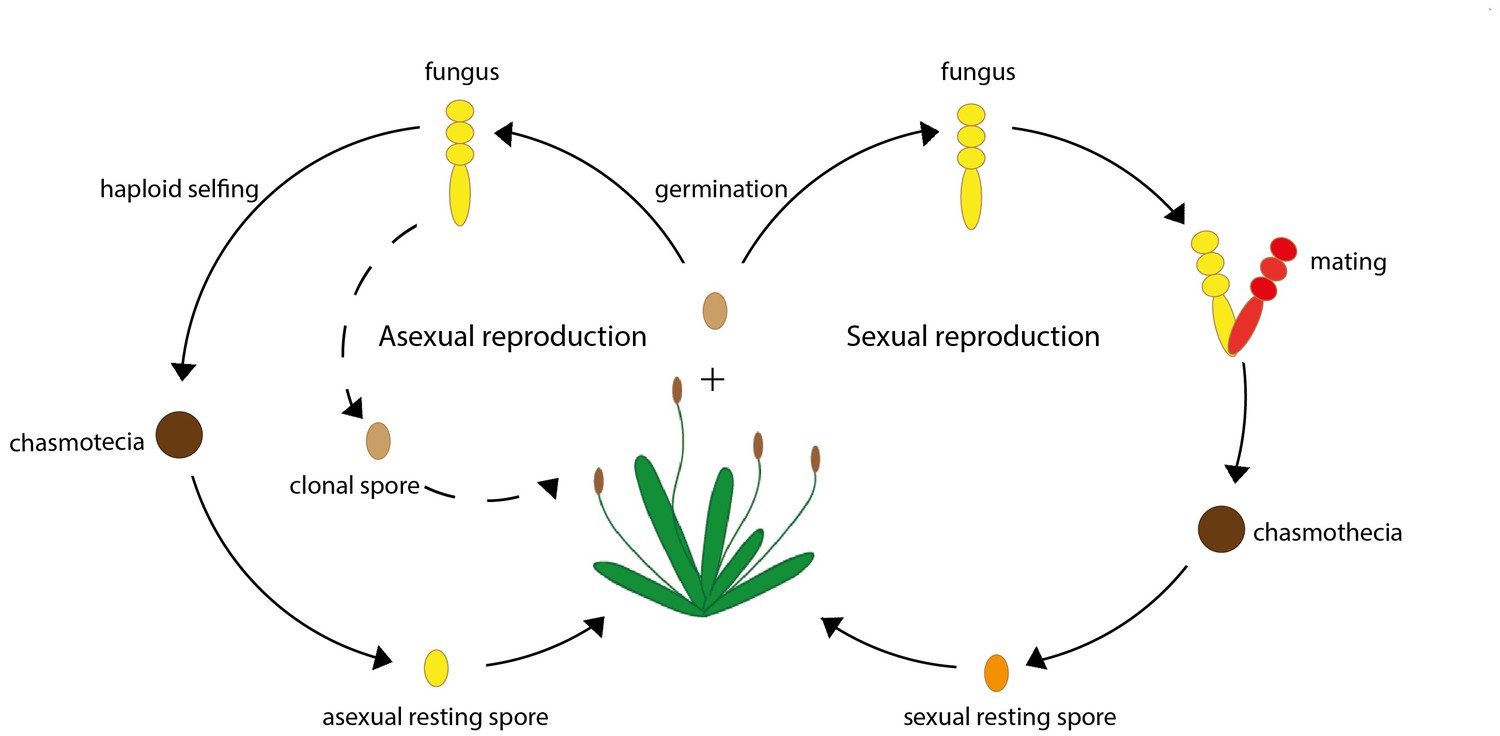
Reproduction Parasites Opt For The Best Of Both Worlds Elife
Solved Fungi Introduction Fungi Are Important Decomposers In Terrestrial Course Hero